Read time 7 mins
Author Josh Wells


Cryptocurrency has been making headlines for years, but it remains a mystery to many. Despite its growing popularity, some people still view it as a risky and unsafe form of payment.
The truth is that cryptocurrencies should be viewed like any investments or payments, so it does come with risks and vulnerabilities. In this blog post, we’ll explore the safety of cryptocurrency and debunk some of the most common crypto safety myths.
By the end of this post, you’ll have a better understanding of the safety of cryptocurrency and know the steps you can take to protect your investments, whether they be in fiat or crypto.
Jump to it:
One of the most common misconceptions about cryptocurrency is that it is used only by criminals for illegal activities. While it is true that some criminals may use cryptocurrency to facilitate illicit transactions, it is essential to note that the majority of crypto users are law-abiding citizens.
According to a report by Chainalysis, less than 1% of all cryptocurrency transactions in 2020 were associated with illegal activities
🚓
Another common myth about cryptocurrency is that it is not secure. While crypto thefts do occur, crypto payments, on the whole, are incredibly secure because they rely on advanced cryptographic techniques that ensure the integrity and security of transactions.
Every crypto transaction on the blockchain is verified and confirmed by a network of nodes, making it extremely difficult to tamper with the transaction history. Moreover, most cryptocurrencies use public-key cryptography, which ensures that only the owner of the private key can access and spend the cryptocurrency. These security measures make it difficult for hackers to steal cryptocurrency, as they would need to gain access to the private key.
The decentralized nature of cryptocurrency also ensures that there is no single point of failure, making it more resilient to attacks and the development of new technologies, such as multi-signature wallets and hardware wallets, has significantly improved the security of cryptocurrency transactions.
Cryptography: A technique used to secure information by encoding it so that only the intended party can read it
Blockchain: The name for the digtal ledger on which most cryptocurrencies live
Digital ledger: a digital ledger records and tracks transactions
Nodes: The moderators of the blockchain ledger. Nodes build the infrastructure of a decentralized network. Anyone can set up a node and start verifying and validating blocks in the network
Decentralized: Not issued by a bank, government, or central authority. Crypto is distributed using a peer-to-peer network
While it is true that cryptocurrency prices can fluctuate significantly in a short period, it is important to note that this is also true for traditional investments such as stocks and bonds.
Cryptocurrency can be a safe investment for a number of reasons.
Fiat: a government-issued currency that is not backed by a commodity such as gold. Fiat gives central banks greater control because they can control how much money is printed. Most modern paper currencies, such as the U.S. dollar, are fiat currencies
One of the most persistent myths surrounding cryptocurrency is that it is a scam or a Ponzi scheme. However, this myth is unfounded and does not reflect the reality of the cryptocurrency industry.
While there are instances of scams and fraudulent projects in the cryptocurrency space, these are not unique to cryptocurrency and many overlap with similar scams robbing people of their fiat currencies.
Like-for-like, fiat currency is used 800X more for money laundering than crypto
⚠️
One of the easiest ways to protect yourself against these kinds of financial scams is to know more about them, so here are some of the most common crypto/fiat scams to watch out for in 2023.
Crypto or fiat, here are some of the most common financial scams to be aware of - have you noticed any of these?
Phishing is one of the most common ways for scammers to access your digital assets. Phishing scams come in many forms; criminals can target users on social media, dating apps and direct messages. However, email links remain among the most prevalent ways hackers harvest sensitive information.
Always be cautious of emails claiming to be from government authorities and well-known businesses, and these are often used to build a sense of trust. While some phishing scams are very sophisticated and can be hard to discern from a genuine email, many have several prominent red flags which can be used to help you discern whether the email is genuine or not.
.gif?width=658&height=494&name=5%20Tips%20To%20Increase%20Your%20Productivity%20Graph%20(6).gif)
Investment scams are very common. Scammers reach out pretending to be investment specialists, enticing users to invest with fictional testimonials and even fake celebrity endorsements.
Often, these kinds of investment scams will ask for an upfront fee, but some will also request personal information, which may give the scammer access to the victim's crypto wallet or bank account.
The easiest way to stay safe from investment scams is simply not to engage with them. If you’re interested in investing your cryptocurrency or fiat currency, then conduct your own research and make a decision using information from trusted sources.
Payment scams are more common in the crypto space because they take advantage of the difficulties crypto users face when trying to pay for things with their cryptocurrency.
Scammers imitate brands, businesses or providers and offer to take crypto as a means of payment which can be appealing to users who usually have to cash out their crypto to pay for goods and services.
Always be cautious when asked to make payments in crypto, even if the email looks to have come from a genuine business and has a link to an official-looking website. If in doubt, always cash out your crypto into fiat currency or cash out onto a gift card and then make your payment via the official business website.
Scammers will go to great lengths to find and manipulate their victims, including using dating apps like Tinder to create fake relationships, which ultimately end in financial theft, blackmail or extortion.
Romance scams can be difficult to spot because scammers are willing to put weeks or even months into building trust with their victims before they ever mention needing money. Here are some red flags to watch out for.
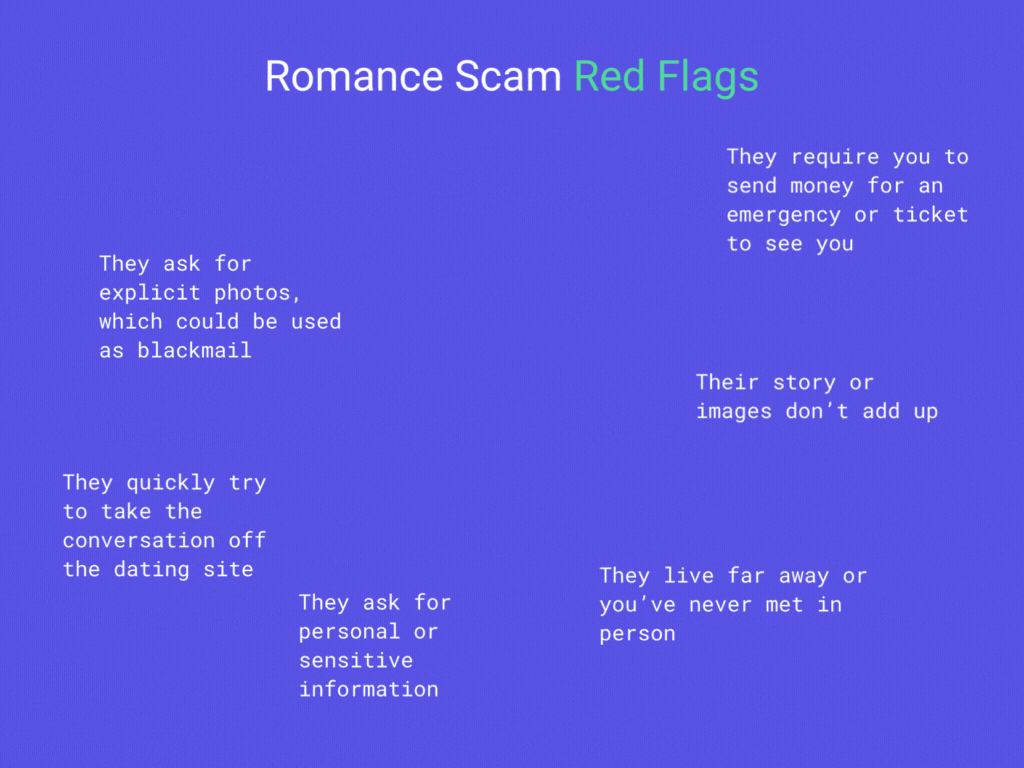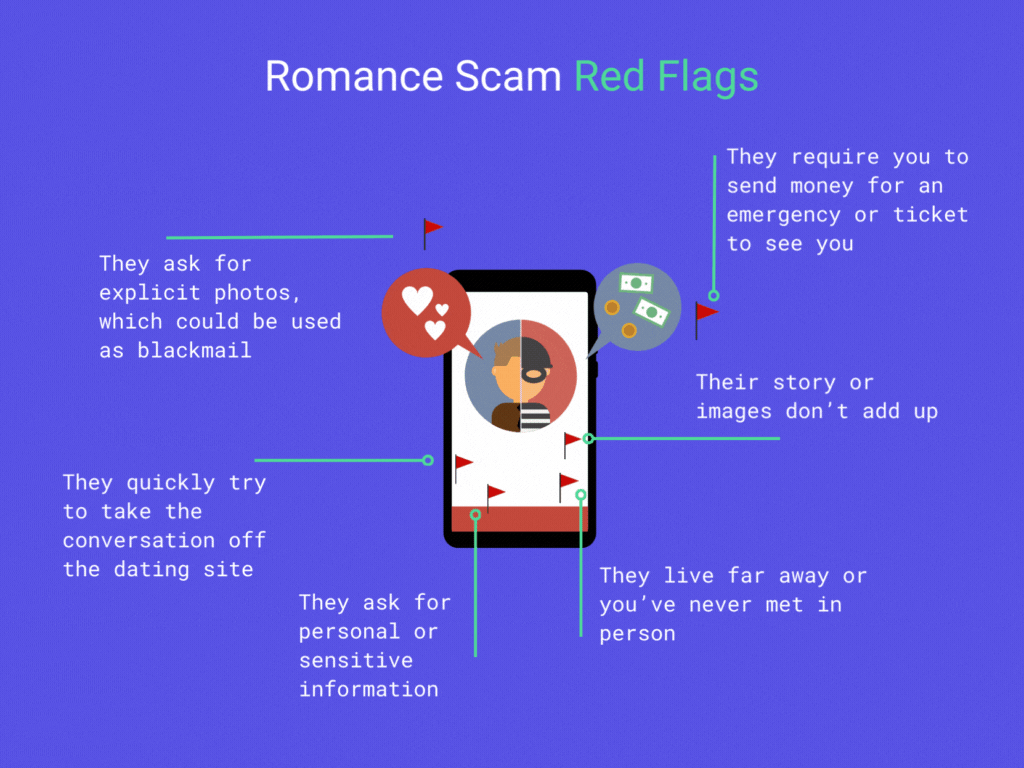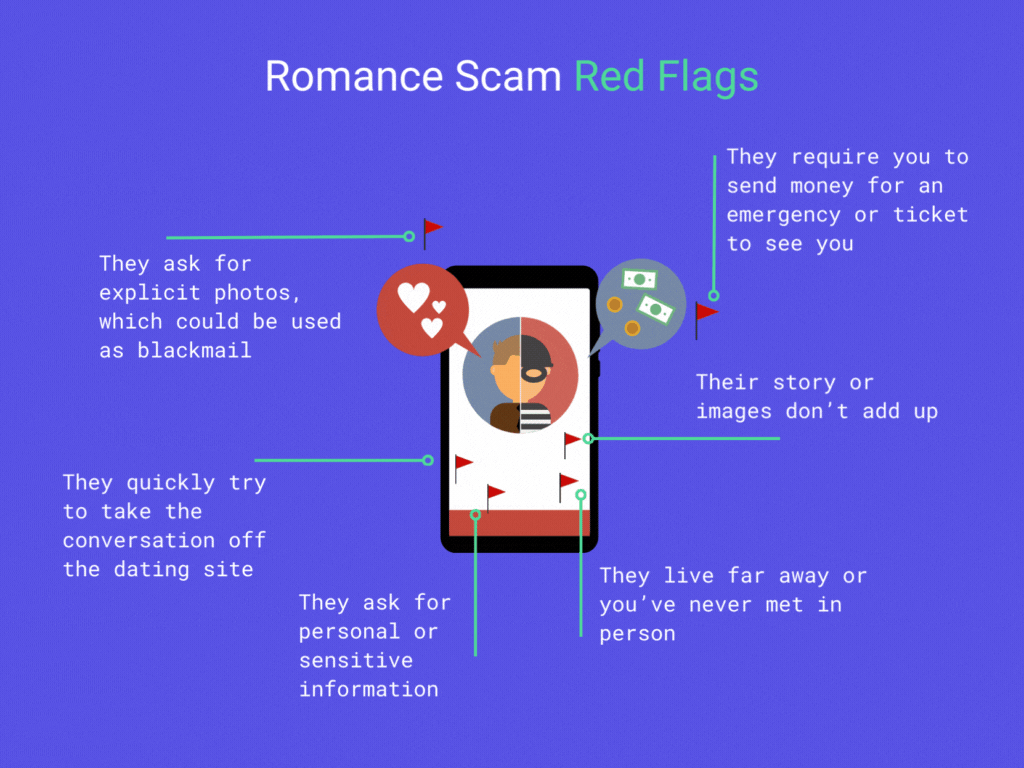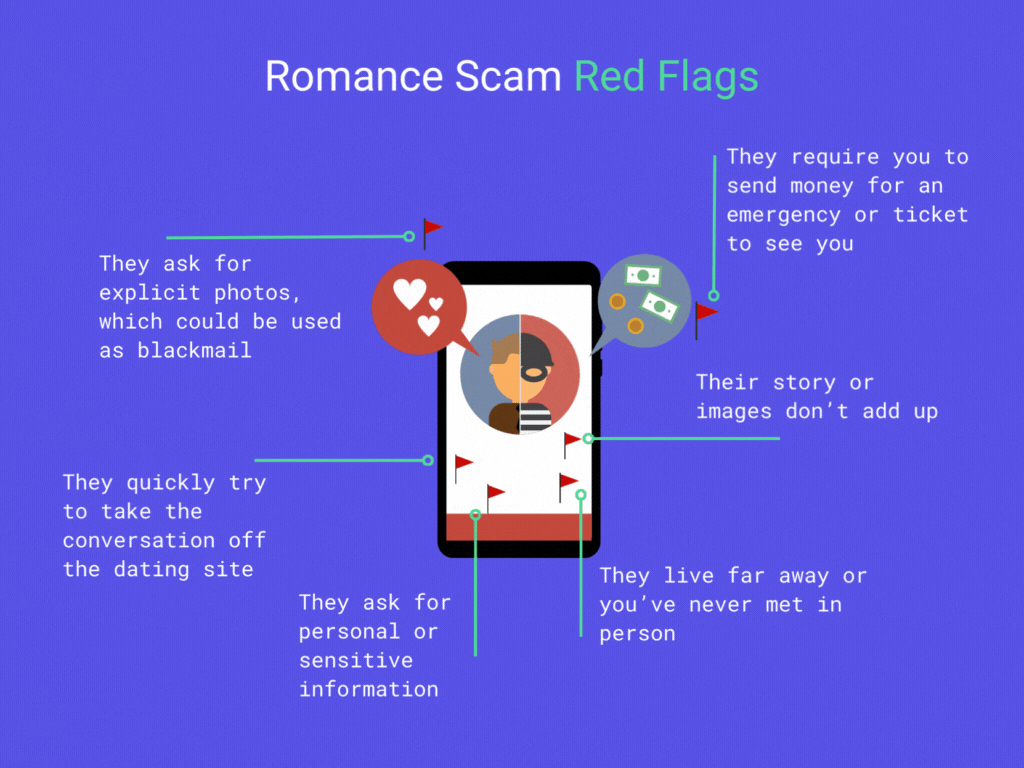
Ponzi schemes lure in their victims with the promise of massive profits at little or no risk. After paying a sign-up fee, buying a course or making an initial investment, the victim will often find themselves recruiting new investors into the scheme keeping it running in circles.
Ponzi schemes are prevalent on social media, where individuals can use videos, images and direct messages to market the scheme to as many people as possible.
In reality, very few people profit from participation in a Ponzi scheme, and most end up leaving, never having made back what they invested.
Like investment scams, fake crypto exchanges often lure their victims in with the promise of valuable investment opportunities. Many have fully fledged brands and may even have fake websites, but in reality, the exchange doesn’t exist, and when the victim hands over their crypto, it is stolen.
The easiest way to avoid this kind of fake exchange scam is to stick with established crypto exchanges like Coinbase and Bitrefil. Not only are established exchanges more reliable, but they may offer additional benefits to their users, such as lower processing fees and alternative cash-out options.
If you want to use a lesser-known exchange, then do your research and be wary of suspicious demands and negative online reviews.
Rug Pull scams are becoming increasingly common, especially relating to nonfungible tokens (NFTs) and new crypto coins, but they’re also found with fiat currency.
Rug Pull scammers create an enticing project, such as a new line of NFTs, designed to lure in early investors. When prices hit a particular ceiling, the project suddenly disappears, and the scammers leave with all of the invested funds.
The Squid Coin scam is one example of a Rug Pull Scam. In the Squid Coin scam, users ‘paid’ to earn a new cryptocurrency boosting the price of a Squid Token from zero to $90. Once the price of this new cryptocurrency was suitably inflated, the developers of the scam shut down the game, fled with the payments and left their victims trying to sell their Squid tokens, whose value had now dropped back to zero.
Man In The Middle attacks target victims using the public network. Scammers intercept information sent over a public network, like the free wi-fi in airports and can use this data to then log into the victim's bank account or crypto wallet and steal their assets.
The easiest way to avoid a Man In The Middle attack is to eliminate the man in the middle by using a Virtual Private Network (VPN); this will encrypt all transmitted data protecting it from thieves and scammers.
VPN: VPN stands for "Virtual Private Network". Using a VPN gives you the opportunity to establish a protected network connection when using public networks.
Giveaway scams are very common on social media, attracting their victims with impressive prizes and, in some cases, false celebrity endorsements.
When the victim clicks on one of these giveaway links, they’re often taken to a website or landing page, which will prompt them to submit payment information that will allow them to ‘receive’ their prize.
Some of these giveaways even charge an entrance fee, and many are also phishing scams in disguise, hiding malicious malware behind the giveaway link. Here are some red flags to watch out for.

Most financial scams are easy to avoid once you know the techniques the scammers use to manipulate their victims.
In summary, here’s how to stay safe from crypto and fiat scams
| 🚫 Don't | ✅ Do |
| Respond to unsolicited contact | Look out for red-flags |
| Click on links without checking their validity | Hover over links to see where they redirect to |
| Use public networks to access your crypto or bank accounts | Practice good digital security & use a VPN |
| Take testimonials at face value |
Use reputable crypto-exchanges |
| Take ‘urgent’ action without thinking first | Cash out before making payments with your crypto |
| Let love cloud your judgement |
Invest cautiously & wisely |
If you come across a financial scam, then you can protect others by reporting it. Reporting scams on social media can help platforms to take down malicious content, and marking spam emails as scams can help your email provider filter out untrustworthy content.
You can also report scams to local law enforcement using the below links. Unfortunately, since a lot of these scams originate from outside of the UK and U.S, law enforcement institutions can only do so much.
Cryptocurrency is a safe and secure form of digital currency that is used by millions of law-abiding citizens around the world. While there have been instances of cryptocurrency hacks and scams, the same can be said for traditional financial institutions, the only difference being crypto receives a lot more bad press and associated fear-mongering.







